Our Approach to Biodiversity
For more than 140 years, the Maruha Nichiro Group has continued its business by making a living from nature's bounty, mainly marine products caught and farmed in oceans. The Maruha Nichiro Group's business also relies heavily on a variety of other natural resources, or ecosystem services, such as agricultural and livestocks , water and soil, and pollinators such as insects.
We recognize that this is an important social issue aiming to contribute to “Nature Positive,” the mission of the Kunming-Montreal Framework for Biodiversity adopted at COP15. An action to halt and reverse the loss of biodiversity in order to put nature on a recovery track. The Maruha Nichiro Group are committed to understanding its dependence on and impact on biodiversity, as well as risks and opportunities, in its business activities throughout the entire value chain, from raw material procurement to product disposal, and to promoting initiatives for its conservation and restoration.
Statement of Support for TNFD (Information Disclosure Policy)
The Maruha Nichiro Group is registered as an adapter to the Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) and is working to disclose information by referring to the disclosure recommendations published by the TNFD in September 2023 in line with the final recommendations (v1.0).
Governance
Maruha Nichiro Group Sustainability Management
Responses to climate change and nature-related issues are promoted mainly by the Sustainability Promotion Committee, which is chaired by the Managing Executive Officer and consists of executive officers with titles who also serve as directors of Maruha Nichiro Co., Ltd., officers in charge of related departments, and heads of related departments, outside directors, and Audit & Supervisory Board members (observers). The Sustainability Promotion Committee plans and sets goals for the overall Maruha Nichiro Group sustainability strategy, and evaluates the activities of each Group company. The Sustainability Promotion Committee meets quarterly four times a year, and each person in charge and project leader report on the progress of each materiality, including the materiality "Biodiversity and Ecosystem Conservation," and actively discuss it. The contents discussed by the Sustainability Promotion Committee are reported and reporting to the Board of Directors through the Management Committee at least four times a year.
We respect human rights in the Maruha Nichiro Group Human Rights Policy, which was formulated in accordance with international standards such as the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, for all people involved in the Group's business, including indigenous peoples, local communities, affected stakeholders, and other stakeholders who are emphasized in their efforts to address nature-related issues. In addition, we conduct human rights training for employees, extract human rights violation risks that may occur in each business activity, including human rights violations against consumers and local residents associated with the consumption of biological capital, and summarize the results in a matrix of severity and likelihood of occurrence as a human rights risk map. These human rights issues, including countermeasures, are reported and discussed by the Sustainability Promotion Committee, and reported to the Board of Directors through the Management Committee.
With the aim of promoting sustainability management, Maruha Nichiro Co., Ltd. has introduced medium-term performance-linked stock compensation that incorporates ESG indicators into the evaluation index for the compensation of management and internal directors. In the medium-term management plan "For the ocean, for life 2027" (FY2025 ~ FY2027), which was announced in 2025, we have set FY2027 targets or FY2030 targets (KPIs) for each materiality, including "biodiversity and ecosystem conservation" and "respect for human rights in business activities," and progress management is carried out, and these progress is also linked to employee personnel evaluation.
Reference Links
Executive Compensation (Coming Soon)
Participation in Initiatives Related to Biodiversity
The Maruha Nichiro Group conducts business through its global supply chain, with marine products at its core. In particular, its procurement activities are closely related to marine resources, and we are concerned that there are many sustainability issues in the broad value chain that cannot be solved by a single company or the private sector alone. To promote comprehensive efforts, we believe it is essential to collaborate with other companies in the industry, government, scientists, and NPO/NGOs. The Maruha Nichiro Group voluntarily participates in various domestic and international initiatives, and reports progress at management meetings and Sustainability Committee meetings.
List of Biodiversity-Related Initiatives Which We Participate
United Nations Global Comapact
Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO)
Clean Ocean Material Alliance (CLOMA)
Japan Business Federation's Biodiversity Declaration
30 by 30 Alliance for Biodiversity
Japan Blue Economy Research Group (BERG)
Participation in Seafood Business for Ocean Stewardship (SeaBOS)
SeaBOS (Seafood Business for Ocean Stewardship) is a global initiative established in 2016 to bring together world's leading seafood companies and scientists studying oceans, fisheries, and sustainability to collaboratively lead science-based strategies and activities to ensure sustainable seafood production and a healthy marine environment.
SeaBOS's activities will actively contribute to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially Goal 14 Protect the richness of the oceans. Currently, six companies are divided into the following five task forces and are discussing solutions to solve them.

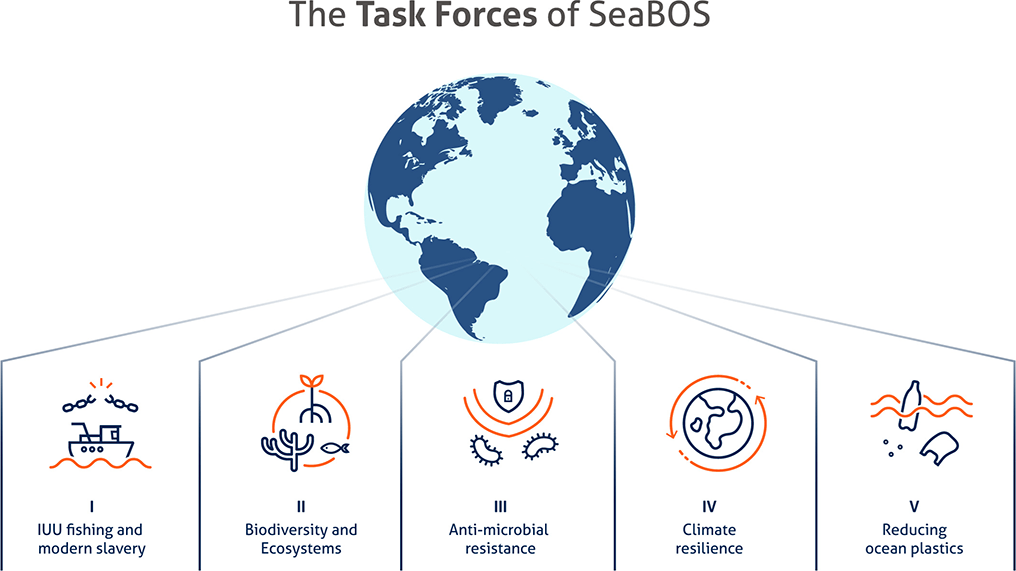
Maruha Nichiro has participated in SeaBOS since its inception, and in September 2018, upon the organization's establishment, our President (at the time), Shigeru Ito, was appointed as the first Chairman and served as Chairman until October 2020. We are currently a co-leader of Task Force V and a member of Task Forces I, III and VI.
Biodiversity-Related Stakeholder Engagement
The marine products handled by the Maruha Nichiro Group have many risks and opportunities. Recognizing the need to eliminate as many risks as possible and maximize opportunities in order to sustainably provide society with valuable protein sources with high health value, we exchanged opinions with external experts with expert knowledge and broad insight on these issues (World Wildlife Fund Japan, General Incorporated Association Ethical Association of Japan) who have expert knowledge and broad insight on these issues.
Dialogue on Sustainable Marine Products

Strategy
Materiality
The Maruha Nichiro Group examines issues from two perspectives: stakeholder interest (importance from a social perspective) and impact on Maruha Nichiro (importance from the company's point of view), and identifies nine priority issues (materiality) in the field of sustainability. Among them, we have identified "response to climate change issues" and "conservation of biodiversity and ecosystems" as materialities related to natural capital and biodiversity.
Reference Links
Identification and review of priority issues (Materiality)
Analysis and Scoping of Biodiversity Dependencies and Impacts Related to Value Chains of All Business Units
One of the materialities, "Biodiversity and Ecosystem Conservation," states that the KGI (2030 vision) "confirms that there is no risk of resource depletion of the marine resources we handle." To achieve this, we conducted an analysis of the dependence and impact of our business on biodiversity in relation to one of the KPIs, "Implementation of Biodiversity Risk Assessment," in accordance with the LEAP approach, which is the guidance advocated by TNFD. Since the Group's value chain is complex and diverse, we identified the biodiversity factors related to the value chain for each business unit (as of 2023), analyzed the degree of dependence and influence on each factor, and narrowed down the targets for further analysis. The target was narrowed down into the following four stages.
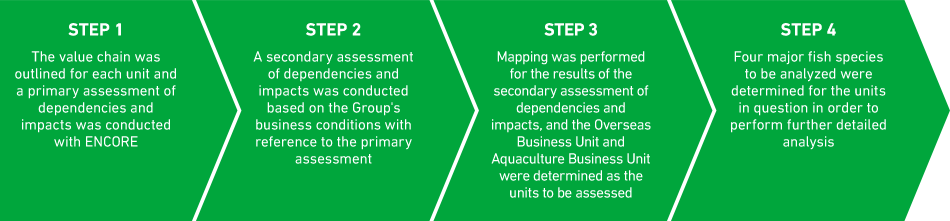
STEP 1–3 Determination of Target Unit
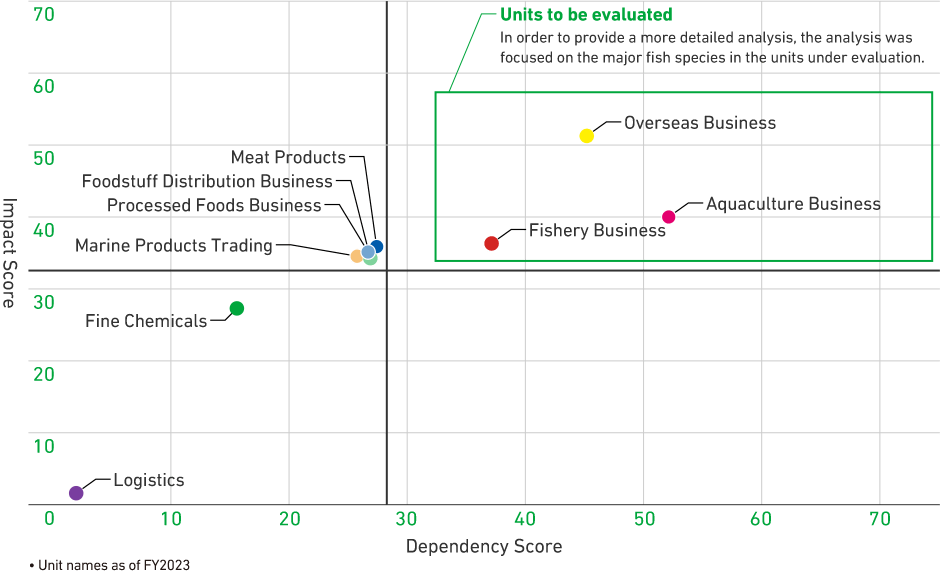
In order to visualize the relationship between business and natural capital, ENCORE*1 conducted a primary assessment of the degree of dependence and influence on natural capital upstream ~ downstream of the value chain of all business units, and then conducted a secondary evaluation of the degree of dependence and influence according to the actual business conditions of the Group. Based on the results of the secondary evaluation of dependence and influence, the score of each unit was calculated*2, and the score of each unit was plotted in the dependence and influence mapping diagram, and as a result of the following figure, the units subject to analysis and evaluation were determined as overseas units and aquaculture units.
- *1
- Geospatial datasets on natural capital assets and environmental change factors, as well as qualitative impact/dependency assessment tools that link ecosystem services to production processes.
- *2
- The 6-level evaluation of NA, VL, L, M, H, and VH by ENCORE is converted into corresponding values (0-5 points), and the number of items in each evaluation along the value chain and directly inside and outside the operation are considered to calculate the dependence and impact score of each unit throughout the value chain.
Reference Data
Dependency and Impact Scores
Step 4 Determination of Fish Species to Be Assessed
Due tolarge number of fish species handled by each unit, target fish species were selected with further analysis. The Overseas Business Unit handled 38% of the Group's wild marine resources and targeted Alaska Pollack, which is also caught by the Group. The Aquaculture Business Unit targeted bluefin tuna, yellowtail, and amberjack, which are the main species of sea-based aquaculture.
Breakdown of Wild Marine Resources/Breakdown of Aquaculture Production (%)
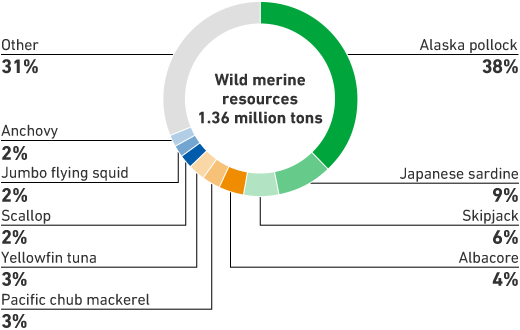
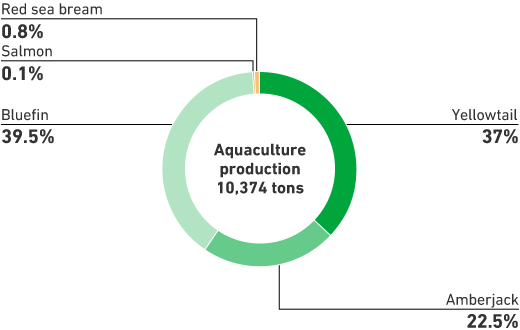
* Breakdown of wild marine resources and breakdown of aquaculture production based on the second marine resources survey (conducted in FY2022)
Reasons for Selecting Target Fish Species and Related Base Areas
| Related business processes | Target fish species | Reason for selection | Target locations/regions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
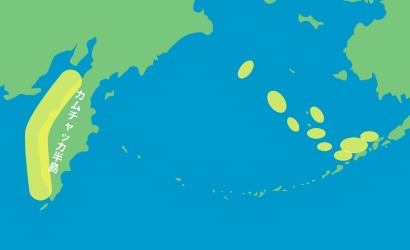
| Overseas Units | Fishery | Whiting | Pollock accounts for 38% of the natural seafood handled and is of high financial importance. | The main fishing areas are the U.S. Bering Sea and the west side of the Kamchatka Peninsula |
| Production and processing are carried out by our own group | ||||
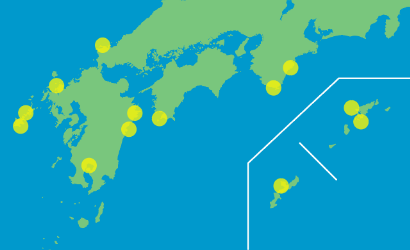
| Aquaculture Unit | Aquaculture | Tuna | The main fish species in the aquaculture unit. | 13 domestic farms |
| Yellowtail | ||||
| Amberjack |
Analysis of Sensitive Locations (Locate)
We analyzed whether the catch and aquaculture areas for each target fish species fall under the "priority areas", which are defined as sensitive locations and material locations under the TNFD guidance.
As a result of analyzing the main pollock fishing areas handled by the Maruha Nichiro Group, the Bering Sea and the western part of the Kamchatka Peninsula, we identified that some or most of the proposed pollock fishing areas may be within or around ecologically and biologically important waters (EBSAs) and protected areas. Based on the above, we have identified all major pollock fishing areas handled by the Maruha Nichiro Group as "priority areas".
As a result of analyzing the 13 farms of the Maruha Nichiro Group in Japan, it was confirmed that 11 fish farms, excluding those in Saeki City, Oita Prefecture and Kagoshima City, Kagoshima Prefecture, fall under the category of highly important sea areas (Ministry of the Environment) from the perspective of biodiversity. We also confirmed that all 13 farms are included in the Marine Protected area (MPA) of the protected planet®. Based on the above, all 13 fish farm bases have been identified as "priority areas".
Confirmed That Alaska Pollock Catch Areas and All 13 Aquaculture Farms Are “Priority Areas”
Analysis of Dependence and Impact of Fisheries (Alaska Pollack) and Aquaculture (Yellowtail, Amberjack, Bluefin Tuna) (Evaluate)
Next, in order to refine the relationship between the relevant dependencies and influences, in addition to the information on dependencies and influences that we researched using ENCORE during the scoping process, we also researched papers, reports, and other sources. As a result, we identified significant dependencies and influences that could lead to risks and opportunities for our business as shown in the table below.
Important Factors Related to Dependency and Impact in Alaskan Pollock Fisheries
| Dependency Impact | factor | (Reference) The magnitude of the impact of ENCORE's evaluation | Why was it judged to be an important factor? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaskan Pollock Fisheries | Impact | Habitat of marine ecosystems | Very High | As assessed by ENCORE, fisheries are important to the habitat of marine ecosystems due to the scale of operations, fishing gear, and fishing methods. Because it may have a negative impact. |
| Natural fish stocks | High | As assessed by ENCORE, overfishing and bycatching have important impacts on the stock status of wild fish and marine ecosystems Because there is a possibility. | ||
| Human rights of fishermen | - | Although not assessed by ENCORE, IUU fishing and others lead to the impact of human rights violations in the supply chain Because there is a possibility. | ||
| dependency | Spawning, growth, habitat | Very High | As assessed by ENCORE, egg production, growth, and habitat have a very strong relationship with the reproduction of individuals of a particular species, and pollock resources are highly dependent on these. | |
| Water quality | Very High | As evaluated by ENCORE, ecosystem services that maintain the chemical state of seawater are the most important factors for marine life to spawn, grow, and survive. It has a great impact on breathing, and pollock's resources depend heavily on these. |
Important Factors Related to Dependency and Impact in Aquaculture
| Dependency Impact | factor | (Reference) The magnitude of the impact of ENCORE's evaluation | Why was it judged to be an important factor? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaculture | Impact | Seabed soil and seawater quality | High | As assessed by ENCORE, in sea surface aquaculture that is directly in contact with marine ecosystems, there is a significant increase in the amount of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) caused by antibiotics and runoff plastics, as well as BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) caused by the habitat of farmed fish. Because the rise is considered an impact to watch out for. |
| Marine ecosystems | High | As assessed by ENCORE, farmed fish are mainly fed by wild fish, and fisheries can have an important negative impact on the habitat of marine ecosystems due to the scale of operations, fishing gear, fishing methods, etc. | ||
| Other farmed fish | High | Although it has not been evaluated by ENCORE, it may affect other farmed fish due to the spread of diseases among farmed fish. Because of his ability. | ||
| dependency | Biologically derived raw materials | Very High | As evaluated by ENCORE, biologically derived raw materials such as natural fish are essential for farmed fish feed. | |
| Water quality (seawater) | Very High | As assessed by ENCORE, deterioration of seawater quality, such as the occurrence of red tides and the increase in BOD (biochemical oxygen demand), greatly affects the productivity of aquaculture. | ||
| Water flow (seawater) | Very High | As assessed by ENCORE, seawater quality has a significant impact on aquaculture productivity, and seawater quality is greatly affected by seawater flow. | ||
| Flood | High | As assessed by ENCORE, floods and storms can cause rapid changes in the aquaculture environment. | ||
| Atmosphere and ground | High | As assessed by ENCORE, sudden changes in the atmosphere and ground (floods, storms, etc.) may cause sudden changes in the aquaculture environment, and climate change is feared to cause an increase in sea temperature, which may change the suitable areas for aquaculture. |
Assessing Method
For key dependencies and impact factors, we identified physical and transitional risks in two scenarios and opportunities in three scenarios. The identified risks and opportunities were evaluated on a five-point scale based on the priority criteria presented by the TNFD in the table. The likelihood of occurrence was evaluated using either the "frequency" or "likelihood" criteria described in the "frequency" or "likelihood" criteria described in the table with reference to the general risk assessment procedure (Risk Management in Practice) commissioned by the Treadway Committee Supporting Organizing Committee (COSO). The intensity and likelihood values were then applied to the financial impact criteria in the table to evaluate the financial impact on a three-point scale.
Financial Impact Assessment Criteria for Risks
| Financial implications | Legal Violations and Lawsuits | Legal Violations and Lawsuits |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable TNFD risk classification | All in particular physical risk transition risks – policy, technology, markets (including consumer-related) | Transition Risks: Liabilities/Liabilities |
| 5 | Quantitative: Impact on ordinary income of 20% or more Qualitative: - Sales and profits will be significantly reduced, significantly undermining the company's profitability and competitiveness in the market. - Significant impact on asset value (additional borrowing, etc. required) - Affects the operation of multiple sites for more than one month | ‐ Large prosecutions and fines ‐ Litigation including class action lawsuits ‐Criminal liability for officers |
| 4 | Quantitative: Impact on ordinary income of 10% or more Qualitative Qualitative: - There was a clear decline in sales and profits, which also affected profitability. - Asset value will be affected. - For more than one month, it will affect the operation of some bases, etc. - Multiple factories affect operations for a few weeks to a month | ‐ Regulatory reporting required, fines and sanctions in business operations are imposed ‐ Large-scale projects required for corrective action |
| 3 | Quantitative: Impact on ordinary income is more than 1% and less than 10% Qualitative: - Sales and profits have declined, affecting profitability. - Some of the asset values will also be affected. - It affects the operation of some factories for a few weeks to one month - Multiple sites affect operations for about one week | ‐ Regulatory reporting is required, and small fines and some sanctions are imposed ‐ Corrective action required |
| 2 | Quantitative: Impact on ordinary income less than 1% Qualitative: - Sales and profits will be affected, and short-term profitability will be slightly reduced. - There is no noticeable impact on asset value. - It will affect the operation of some factories for about one week - Multiple locations affect operations for days | ‐ Regulatory reporting required ‐ It does not result in fines or legal action, but requires certain follow-up |
| 1 | Quantitative: Almost no concrete financial impact Qualitative: - There will be a slight impact on sales and profits, but only a slight decrease in short-term profitability. - There is no noticeable impact on asset value. - Affects the operations of some bases, etc., but to a negligible extent | ‐ Violation of internal regulations ‐ No special regulatory action required |
Financial Impact Criteria for Opportunities
| Financial implications | Legal Violations and Lawsuits | Legal Violations and Lawsuits |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable TNFD risk classification | Resource Efficiency Improvement, Product and Service Markets, Capital Flows & Financing Sustainable use of natural resources, protection, restoration and restoration of ecosystems | judge Capital Flow & Financing |
| 5 | ‐ Significant Cost Savings: Successful initiatives can result in significant reductions in operational and production costs (e.g., significant cost savings through improved energy efficiency or resource recycling). - Creating high-profit new business: sustainable products and services as a new revenue stream - It is likely that the market will succeed and generate significant revenue. | ‐ It is widely covered in a wide range of media globally, and the brand image of companies and organizations is dramatically improved. ‐Establishing industry standards and leadership in sustainability. |
| 4 | ‐ Notable Cost Savings: Successful initiatives, such as energy efficiency enhancements and waste management improvements, can result in reduced annual operating costs. - New revenue streams: New sustainable products and services are well received in the market, and new - Establish a source of revenue. | ‐ It will be reported in many domestic and foreign media, and the brand image of the company will be greatly improved. ‐ Sustainable initiatives are recognized both inside and outside the industry and receive certain recognition. |
| 3 | ‐ Moderate Cost Savings: Certain cost savings can be expected, but the impact is moderate. - Ancillary revenue streams: Sustainable new products and services gain a certain market share and generate revenue, but they account for a small percentage of overall revenue. | ‐ There is a certain amount of media coverage in Japan, and the brand image is improved in some areas. ‐ Sustainable initiatives are recognized within the industry and receive certain recognition. |
| 2 | ‐ Small-scale cost savings: Efforts are made, but the cost savings are limited (e.g., employee training programs or small process improvements). - Limited Revenue: New sustainable products and services are introduced to the market, but their contribution to the bottom line is negligible. | ‐ Although it is covered in limited media, the improvement of the brand image is limited. ‐ Sustainable initiatives are recognized only by a few stakeholders. |
| 1 | ‐ Smallest cost savings: The cost savings from your efforts are minimal. - No revenue contribution: New sustainable products or services are introduced to the market but do not lead to monetization. | ‐ There is little media exposure, and the impact on brand image and recognition is negligible. |
Evaluation Criteria for the Likelihood of Occurrence
| Judging criteria | ||
|---|---|---|
| scale | frequency | possibility |
| 5 | Multiple times a year | Almost certainly |
| 4 | About once a year | (Obviously) high |
| 3 | Once every 1~3 years | (more likely to occur) Medium |
| 2 | Once every 3~5 years | There is a possibility (although not expensive) |
| 1 | Once every 5~10 years | (Obviously) low |
Financial Impact Judgment Criteria

Scenarios to Use for Valuation Analysis
The scenario selection and analysis assumed four quadrants (#1~#4) based on two axes, namely the degree of degradation of nature and ecosystems recommended by the TNFD framework and the response of the sustainable market (a market that prefers sustainable products), and considered the scenarios to be adopted.

Adoption Scenario and Risk Analysis Results in Alaskan Pollock Fisheries
Since Alaskan pollock fisheries are already under strict resource management and can fully anticipate scenarios with low degradation of nature and ecosystems, we adopted scenario #1 (minor degradation of nature and ecosystems, consumers prefer sustainable products) and scenario #3 (severe degradation of nature and ecosystems, and consumers do not allow sustainable products to penetrate the market). Assuming scenario #3, we assessed that the financial impact would be high for three migration risks, in particular. Although Alaskan pollock is a resource that is strictly managed as a resource, if the stock and catch decrease significantly due to external influences such as rising sea temperatures in the future, it is thought that the risk of transition, such as strengthening fisheries regulations, will increase.
* This table is scrollable.
| Dependency and impact | Important factors | Physical risk: Risks caused by physical factors such as natural disasters Transition risk: Risks that arise when companies try to adapt to the environment and transition to sustainability | Scenario #1 The deterioration of nature and ecosystems is minor. Limited degradation of resource state The rise in sea temperature is also limited. Consumers prefer sustainable products | Scenario #3 Nature and ecosystems are degraded Resource conditions deteriorate Deterioration of water quality due to rising sea temperature Sustainable products do not penetrate the market (price-oriented) | ||||||||
| Size of risk | Possibility of occurrence | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | Size of risk | Possibility of occurrence | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | |||||
| Alaskan pollock fisheries | Impact | Habitat of marine ecosystems | Migration risks | Policy | 1 | 1 | Low | Overfishing is strongly regulated, and the environmental impact is not enough to affect wild seafood. Stocks and catches are maintained. | 4 | 3 | High | Due to external influences such as rising sea temperatures, the amount of stocks and catches is significantly reduced. |
| Natural fish stocks | Market/Reputation | 1 | 2 | Low | According to the scenario setting, the amount of natural seafood resources remains unchanged and the catch is maintained. On the other hand, changes in the habitat environment due to rising sea temperatures are becoming apparent, and the impact on fish catches cannot be denied. | 4 | 5 | High | Due to changes in the habitat environment such as rising sea temperatures, the amount of pollock resources is significantly decreasing, and business profits will deteriorate significantly. | |||
| Human rights of fishermen | Liability | 3 | 3 | Medium | The amount of aquatic resources will not change, but from the perspective of stronger ecosystem protection, the restrictions on catch quotas and fishing areas will be stricter, and profitability will decrease to a certain extent. There is a possibility that it will be. | 4 | 4 | High | Against the backdrop of a significant decrease in the amount of marine resources, there is a possibility that strong regulations such as catch restrictions and bans on pollock fishing may occur. | |||
| Dependency | Spawning, growth, habitat | Physical risks | Acute | 1 | 3 | Low | Consumers are becoming more inclined to prefer more sustainable products, and additional costs such as expanded certifications are incurred to meet market needs, but the negative impact on profitability is minor. | 2 | 4 | Medium | Although there is an impact on prices due to the decrease in stocks, since it is a cheap fish species, it is assumed that the price will not be so high that it will be shunned by the cost-oriented market around 2030, and the degree of deterioration in profits is limited. | |
| Water quality | Chronic | 2 | 1 | Low | Maruha Nichiro and its procurement companies are in strict compliance with laws and regulations, and the possibility of non-compliance is extremely low. | 2 | 1 | Low | Maruha Nichiro and its procurement companies are in strict compliance with laws and regulations, and the possibility of non-compliance is extremely low. (However, IUU fishing products are rampant in the market, and untraceable procurement may include IUU products.) | |||
Aquaculture Adoption Scenarios and Risk Analysis Results
Aquaculture is highly dependent on wild fish for feed, and the catch of wild fish involved in feed is declining, so we adopted scenario #2 (significant degradation of nature and ecosystems, consumers prefer sustainable products) and scenario #3 (significant degradation of nature and ecosystems, and consumers do not penetrate the market for sustainable products). In both scenarios, we assessed that the financial impact will be high for the three physical risks. As a chronic risk, it was assumed that the cost of procuring naturally derived feed would increase due to the decrease in the amount of natural resources in the ocean, or that profitability would deteriorate due to the increase in the development and procurement costs of alternative feed. In addition, as an acute risk, it was assumed that profitability would decrease due to deterioration in the growth of farmed fish due to changes in the environment of aquaculture farms, and that the cost of repairing damage to facilities due to weather disasters would increase.
Aquaculture Scenario Risk Analysis Results
* This table is scrollable.
| Dependency and impact | Important factors | Physical risk: Risks caused by physical factors such as natural disasters Transition risk: Risks that arise when companies try to adapt to the environment and transition to sustainability | Scenario #2 ・Nature and ecosystems are degrading ・Natural resource conditions are deteriorating ・Water quality deterioration due to rising seawater temperatures ・Consumers prefer sustainable products | Scenario #3 ・Nature and ecosystems deteriorate ・Resource conditions worsen ・Water quality deteriorates due to rising seawater temperature ・Sustainable products do not penetrate the market(Price-focused) | ||||||||
| Aquaculture | Size of risk | Possibility of occurrence | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | Size of risk | Possibility of occurrence | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | ||||
| Impact | Seabed soil and seawater quality | Migration risks | Policy | 2 | 2 | Low | Tightening regulations to protect coastal ecosystems and forcing fish farms to move will result in temporary capital expenditure and increased operating costs. On the other hand, the market accepts price pass-on for environmental conservation, so the impact on profitability is transitory | 2 | 3 | medium | Tightening regulations to protect coastal ecosystems and forcing fish farms to move will result in temporary capital expenditure and increased operating costs, which will worsen profitability | |
| Marine ecosystems | Reputation | 2 | 2 | Low | Consumers prefer more sustainable products, which requires stronger measures to align with the demand for alternative proteins with a lower environmental impact. | 3 | 3 | medium | The market share of sustainable high-priced goods decreases and sales decline. | |||
| Other farmed fish | ||||||||||||
| Dependency | Biologically derived raw materials | Physical risks | Acute | 3 | 3 | Medium | Due to changes in the environment of fish farms, increased drug use, increased management costs, and reduced quality lead to a decrease in profitability. | 2 | 2 | medium | In response to the increased risk of infection such as fish diseases due to environmental changes in aquaculture farms, increased drug usage and increased management costs contribute to a decline in profitability (drug use is not considered important to the market. ) | |
| Chronic | 3 | 4 | High | It is assumed that the catch of non-edible fish will decrease as the amount of natural resources in the ocean is declining and catch restrictions will be tightened. As a result, the procurement of natural feed or the development and procurement of alternative feed requires costs, and profitability deteriorates. | 3 | 4 | High | It is assumed that the catch of non-edible fish will decrease as the amount of natural resources in the ocean is declining and catch restrictions will be tightened. As a result, the procurement of natural feed or the development and procurement of alternative feed requires costs, and profitability deteriorates. | ||||
| Water quality (seawater) | Acute | 3 | 4 | HIgh | Due to changes in the environment of the farm, the growth of farmed fish will deteriorate, and the profitability will decrease to a certain extent. | 3 | 4 | High | Changes in the environment of farms will worsen the growth of farmed fish, reducing profitability to a certain extent. | |||
| Water flow (seawater) | Acute | 4 | 2 | High | Weather disasters have devastated fish farms, requiring a reasonable period of time to restore facilities and biological assets. | 4 | 2 | HIgh | Weather disasters have devastated fish farms, requiring a reasonable period of time to restore facilities and biological assets. | |||
| Flood | ||||||||||||
| Atmosphere and ground | ||||||||||||
Opportunity Analysis Results of Adoption Scenarios in Pollock Fisheries and Aquaculture
Regarding opportunities, we analyzed all scenarios #1 and #3 for pollock fisheries, scenarios #2 and #3 for aquaculture, and #1, #2, and #3 for common ones. As a result, we assume that our opportunities are greater if consumers prefer sustainable products in scenarios #1 or #2, but the financial impact on us if sustainable products do not penetrate consumers will be limited. Based on the above, we believe that the penetration of sustainable products into the market will positively contribute to the Company's financial impact.
Opportunity Analysis Results of Recruitment Scenarios
* This table is scrollable.
| Opportunity categories | Expected opportunities | Scenario #1 ・Minor degradation of nature and ecosystems. ・Limited deterioration of resource conditions ・Limited rise in seawater temperature ・Consumers prefer sustainable products | Scenario #2 ・Nature and ecosystems are deteriorating ・Natural resource conditions are worsening ・Water quality deterioration due to rising seawater temperatures ・Consumers prefer sustainable products | Scenario #3 ・Nature and ecosystems are degraded ・Resource conditions are deteriorating ・Water quality deterioration due to rising seawater temperature ・Sustainable products do not penetrate the market (price-focused) | ||||||||||
| Opportunity size |
Occurrence possibility | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | Opportunity size |
Occurrence possibility | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | Opportunity size |
Occurrence possibility | Financial impact | Maruha Nichiro's view | |||
| Alaska pollock fishery | Market | Opportunities to increase sales due to market development and reputational improvement due to changing consumer orientation for products with lower environmental impact | 4 | 4 | High | As the ethical market grows rapidly, the demand for our sustainable products will increase, and we believe that a significant opportunity will arise | 1 | 1 | Low | There has been no noticeable change in demand for sustainable products, and although it continues to appeal to the market, its contribution to sales is limited. | ||||
| Resource efficiency | Stabilization of fisheries business due to the promotion of sustainable procurement through fisheries with low environmental impact | 3 | 4 | High | Sustainable fisheries implemented under strict legal compliance maintain marine resources and contribute to business stability. | 3 | 2 | Medium | Sustainable fisheries implemented under strict legal compliance maintain marine resources and contribute to the stabilization of business. However, it is not easy to prevent the decrease in resource quantities due to external factors such as rising sea temperatures, and the cost benefits have limited possibilities. | |||||
| Products & Services | Opportunities to increase sales due to market development and reputation improvement by effectively using waste raw materials (residues) into meal (fishmeal) | 2 | 3 | Medium | The demand for farmed fish and farmed feed will increase on the back of tighter fishing regulations and population growth, which will increase the demand for sustainable fishmeal. | 3 | 3 | Medium | With the decline in natural resources, the demand for fishmeal will grow on the back of increasing demand for farmed fish and farmed feed. | |||||
| Aquaculture | Resource efficiency | Cost savings due to reduced use of natural resources due to increased feed conversion rates(note needed) | 3 | 3 | Medium | Since it does not own a feed production division, it is unlikely that it will develop advanced and innovative technologies significantly compared to other companies, but it is judged that some opportunities can be expected | 3 | 3 | Medium | Since we do not own a feed production division, it is unlikely that we will develop advanced and innovative technologies significantly compared to other companies, but we believe that we can expect some opportunities | ||||
| Products & Services | Opportunities to increase sales due to upfront investment and market position | 3 | 3 | Medium | As the ethical market grows rapidly, the demand for our sustainable products will increase, and we believe that there will be a huge opportunity. | 2 | 2 | Low | There is no noticeable change in demand for sustainable products, and the return on investment is limited | |||||
| Market | Opportunities to increase sales due to market development and reputational improvement due to changing consumer orientation for products with lower environmental impact | 3 | 3 | Medium | The market for farmed fish will expand as the amount of natural resources decreases, and the demand for the company's sustainable products in particular is expected to grow significantly. | 2 | 2 | Low | The market for farmed fish expands as the amount of natural resources decreases. On the other hand, in markets that prefer cheaper products, the share of sustainable products will be limited | |||||
| Market | Changes in fish species due to rising sea temperatures led to an increase in sales of alternative protein raw materials (cell cultures) | 4 | 4 | High | As the ethical market grows rapidly, the demand for sustainable products will increase, and we believe that a significant opportunity will arise | 3 | 3 | Medium | The demand for alternative proteins is also increasing on the back of increasing overall protein demand. Consumers prioritize cost performance, so low price and high quality contribute to increased sales. | |||||
| Market | Opportunities to increase sales due to increased production due to investments in improving aquaculture environments | 3 | 3 | Medium | In a market with advanced ethical consumption, the pass-through of investment costs is acceptable, and the increase in production contributes to sales. | 2 | 3 | Medium | Passing on investment costs to prices is unacceptable, and cost benefits are limited | |||||
| Common | Market | Opportunities for stock price appreciation due to improved valuation from investors due to improved corporate valuation ratings | 2 | 3 | Medium | ESG ratings have a significant impact on investment decisions and contribute to the rise in stock prices. | 3 | 3 | Medium | ESG ratings have a significant impact on investment decisions and contribute to the rise in stock prices. In addition, the decline in resource quantities and the increase in demand for protein are tailwinds, and the willingness to invest in the food sector is high. | 1 | 3 | Low | The impact of ESG ratings on investment decisions is not very significant, and the contribution to stock prices is limited. |
| Capital flows and Capital | Reducing the cost of capital through access to green investment markets | 3 | 3 | Medium | The impact on the cost of capital was assumed to be limited | 3 | 3 | Medium | The impact on the cost of capital was assumed to be limited | 1 | 2 | Low | As a scenario setting, investors prioritize financial growth | |
| Reputation capital | Opportunities to increase sales due to market development and reputational improvement through collaboration with regional stakeholders, such as the development of blue carbon credits and the removal of marine plastic pollution. | 3 | 3 | Medium | ESG evaluation is also important in the market and contributes to sales to a certain extent. | 3 | 3 | Medium | ESG evaluation is also important in the market and contributes to sales to a certain extent. | 1 | 2 | Low | The market does not consider initiatives that do not affect cost performance. | |
Managing Risk and Impact
With regard to company-wide risk management in the Group's business activities, we have established a system in which risk management managers and risk management personnel from each department of Maruha Nichiro Co., Ltd. and Group companies work together to manage company-wide risk management in the course of the Group's business activities. Short-term and high-impact risks related to the environment and sustainability are identified, analyzed, and countermeasures are identified and analyzed through the annual risk management program, and reported to the Management Committee.
In addition, medium- to long-term risks and opportunities related to ESG and sustainability are managed and discussed by the Sustainability Promotion Committee. In particular, risks related to climate change and biodiversity are considered as one of the important risks, and risks and opportunities analyzed and evaluated through scenario analysis based on the TCFD framework and TNFD's LEAP approach are managed and discussed.

Indicators, Targets and Related Results (Prepare)
Indicators and targets based on risk and opportunity analysis
Maruha Nichiro has set the following indicators and targets (KPIs) to solve the identified risks and opportunities. By working to achieve these KPIs, we aim to reduce risks and maximize opportunities.
* This table is scrollable.
| Maruha Nichiro's view on important dependencies, impacts, and risks | Important issues related to risk | Basic approach to Material issues | Maruha Nichiro's initiatives | Related KPIs | ||||
| Alaskan pollock fisheries | Although resource management is quite strict, a decrease in the amount of resources due to external factors such as rising sea temperatures will lead to a negative financial impact on the Company and will also lead to restrictions on resource access for local residents in the fishing area. | Decrease in resource volume due to external influences, such as rising sea temperatures. | While continuing business activities based on strict fisheries management, we will also strive to prevent the decline of stocks due to external influences through participation in international initiatives | Operate in accordance with strict fishing regulations in the U.S. Bering Sea (e.g., restrictions on fishing areas, quotas, timing, gear, and fishing methods) | Procurement of marine products derived from MSC-certified fisheries (Bering Sea, Kamchatka West, U.S.) | Conducting Fisheries Resource Surveys | Efforts in Task Force IV at SeaBOS | ・100% of the resource status confirmation rate of marine resources handled by the end of FY2030 (all global consolidated subsidiaries) |
| Protection of the rights of fishermen | Since these resources are important resources for local residents, we will continue our business activities based on strict fisheries management | Operate in accordance with strict fishing regulations in the U.S. Bering Sea (e.g., restrictions on fishing areas, quotas, timing, gear, and fishing methods) | Procurement of marine products derived from MSC-certified fisheries (Bering Sea, Kamchatka West, U.S.) | Formulation of a sustainability-friendly seafood procurement policy | ||||
| Aquaculture | The risks caused by factors related to dependence on biological capital are large and need to be addressed with focus. | Decrease in the amount of natural fish stocks used in feed | It is urgent to grasp the amount of natural fish resources in feed, and after understanding the amount of resources, efforts should be made to appropriately manage the resources of each resource | Conducting Fisheries Resource Surveys | Establishment of self-management standards for fish farms | Acquisition of ASC certification for Buri Amberjack | ・100% of the resource status confirmation rate of marine resources handled by the end of FY2030 (all global consolidated subsidiaries) | |
| Responding to the deterioration of seawater quality due to red tides, etc. | Responding to changes in seawater quality and sea temperature is important for business continuity, and the development of new aquaculture technologies, such as the introduction of large-scale floating and sinking copper alloy cages, is important | Introduction of a large floating and sinking copper alloy cage in consideration of the breeding environment of farmed fish. | ・Establishment of | |||||
| Strengthening Resilience to Weather Disasters | In order to respond to this important issue, it is necessary to develop aquaculture technology | Introduction of a large floating and sinking copper alloy cage in consideration of the breeding environment of farmed fish. | Beginning of cedar farming | a certification level management system for all aquaculture farms within the Group by the end of 2027 (domestic consolidated subsidiaries) | ||||
* This table is scrollable.
| Maruha Nichiro's view of opportunity | Important issues related to risk | Basic Approach to Material Issues | Maruha Nichiro's Initiatives | Related KPIs | |||
| Alaskan pollock fisheries | If scenario #1 goes as planned, the positive financial impact on the company will be significant. Since resource management is strict, the key is for the market environment to be positive for the transition to nature-positive. | Fostering an ethical market | In order to foster an ethical market, it is important to spread understanding of sustainable seafood*among consumers. | Providing food that contributes to health value creation and sustainability | ・By the end of FY2030, marine products | ||
| Maintaining the amount of resources | Business activities based on strict fisheries management contribute to business stability | Operate in accordance with strict fishing regulations in the U.S. Bering Sea (e.g., restrictions on fishing areas, quotas, timing, gear, and fishing methods) | Procurement of marine products derived from MSC-certified fisheries (Bering Sea, Kamchatka West, U.S.) | Formulation of a sustainability-friendly seafood procurement policy | ・Sustainable seafood (sustainably certified products) sales ratio of all products, including marine products, will be 15% or more (Maruha Nichiro Co., Ltd.) | ||
| Aquaculture | If scenario #1 goes as planned, the positive financial impact on the company will be significant. When the market environment becomes positive for the transition to nature-positive, it is important to create a system to meet the demand. | Expansion of ASC certification | If things don't go as in Scenario #1, the cost benefits will be limited, as investment costs cannot be expected to be passed on, but it is important to prepare a supply system to meet market demand | Conducting Fisheries Resource Surveys | Establishment of self-management standards for fish farms | Acquisition of ASC certification for Buri Amberjack | ・100% of the resource status confirmation rate of marine resources handled by FY2030 (all global consolidated subsidiaries) |
| ・Establishment of a certification level management system for all aquaculture farms within the Group by the end of 2027 (domestic group consolidated subsidiaries) | |||||||
| Commercialization of cellular marine products | It is necessary to prepare a supply system to meet market demand. | UMAMI Bioworks and the development of cellular bluefin tuna | ・Sustainable seafood (sustainably certified products) sales ratio of all products, including marine products, 15% or more (Maruha Nichiro Co., Ltd.) | ||||
*Certified seafood approved by the Global Sustainable Seafood Initiative (including MSC certification, ASC certification, BAP certification, MEL certification, etc.)
Core Disclosure Indicators
Table Information Based on Core Disclosure Indicators (Pollock Fisheries and Aquaculture)
* This table is scrollable.
| Global/Sector | TNFD Metric No. | Subcategories / Drivers | index | status quo |
| Global | ー | climate change | GHG emissions | Environmental Data |
| (Domestic G) | ||||
| C1.0 | Changes in the use of land, freshwater and oceans. | Spatial footprint (km2) | FAO Area 61,67 | |
| (Pollock Fishery) | ||||
| 56,439m2(Land area) 389,002m2(Fishing area) | ||||
| (aquaculture) | ||||
| C2.1 | Contamination / Decontamination | drain | Environmental Data | |
| (Domestic G) | ||||
| C2.2 | Generated weight by hazardous and non-hazardous waste type | Environmental Data | ||
| (Domestic G) | ||||
| C3.0 | Use and replenishment of resources | Water withdrawal and | Environmental Data | |
| consumption from water-scarce areas considering water sources (m3) | (Domestic G) | |||
| C3.1 | Use and replenishment of resources | Quantity of | Results of resource survey of marine products handled | |
| high-risk natural commodities | ||||
| sourced from land, ocean, and freshwater bodies | ||||
| Percentage of total catches caught from sustainably managed resources | Results of resource survey of marine products handled | |||
| C4.0 | Invasive alien species and others | Countermeasures against the introduction of unintentional invasive alien species (IAS) | All MSC certified fisheries | |
| (pollock fishery) | ||||
| C5.0 | Natural state | Species extinction risk | Results of resource survey of marine products handled | |
| C7.0 | Migration risks | Percentage of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses assessed as vulnerable to natural capital-related transition risks | Scenario Risk Analysis | |
| Results (Pollock Fishery) | ||||
| C7.1 | Physical risks | Percentage of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses assessed as vulnerable to natural capital-related physical risks | (Aquaculture) | |
| C7.2 | Transition Risks - Responsibilities | Details of serious fines and lawsuits incurred in the reporting year and the cost of responding to negative natural impacts | N/A in the past 3 years | |
| (pollock fishery) | ||||
| N/A in the past 3 years | ||||
| (aquaculture) | ||||
| C7.3 | Opportunity | Capital expenditures and financing by opportunity type or investment deployed for nature-related opportunities | Issuance of Blue Bond | |
| (MN) | ||||
| C7.4 | Opportunity | Percentage of sales of certified products approved by GSSI among products containing seafood | FY2024 6.4% | |
| (MN) | ||||
| C7.4 | Opportunity | ー | All MSC certified fisheries | |
| (pollock fishery) |
*Target organizations are abbreviated as MN = Maruha Nichiro Co., Ltd., Domestic G = Domestic Group Consolidated Company, G Overall = Global Consolidated Company, Overseas G = Overseas Group Consolidated Company







